Raw Milk Quality Testing for Identifying Microbial Contamination Sources
One key step to monitoring raw milk quality is raw milk microbial testing, a meticulous monitoring process that examines raw milk’s microbiological parameters. Using QualiTru’s sampling systems, such as the TruStream Septa and TruStream Ports, allows for effective process monitoring for issues such as somatic cell counts (SCC), milk stratification, spore-forming bacteria, and bacterial counts to help ensure superior dairy product production. The ability to identify and isolate bacteria, including heat-resistant bacteria, is vital to safe and efficient operations for milk processors.
Raw Milk Quality Testing and Finished Milk Quality
Impact on Quality and Shelf Life: Raw milk quality significantly influences finished milk products, including their quality and shelf life. Factors such as enzymes, bacterial spores, and microbial load from raw milk can persist through processing and affect pasteurized milk. High somatic cell counts and bacterial contaminants can also contribute to lipolysis, proteolysis, and spoilage, leading to off-flavors and reduced shelf life.
Contamination Levels and Storage: To achieve an extended shelf life, dairy processors must maintain low bacterial counts in pasteurized milk. This requires efficient sanitation practices and cold storage to delay microbial growth, ensuring a shelf life greater than 14 days. Maintaining low initial inoculum levels and appropriate refrigeration temperatures can help retain the quality and stability of dairy products .
QualiTru’s representative sampling system is approved for use by the Pasteurized Milk Ordinance (PMO). See Regulatory Approvals.
Importance of Microbiological Sampling in Dairy Plants
- Processing Challenges: Dairy plants face challenges in maintaining high quality due to fast-paced, high-volume operations. Contamination, even at low levels, can impact fluid milk quality, causing sporadic spoilage and making it hard to track.
- Sources of Contamination: Improperly cleaned equipment, inadequate maintenance, and biofilms contribute to post-pasteurization contamination. Equipment like tanks, pipes, and fillers require careful monitoring.
- Comprehensive Approach: A Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) system with microbiological sampling at critical points can help identify and manage contamination, ensuring quality control throughout the process.
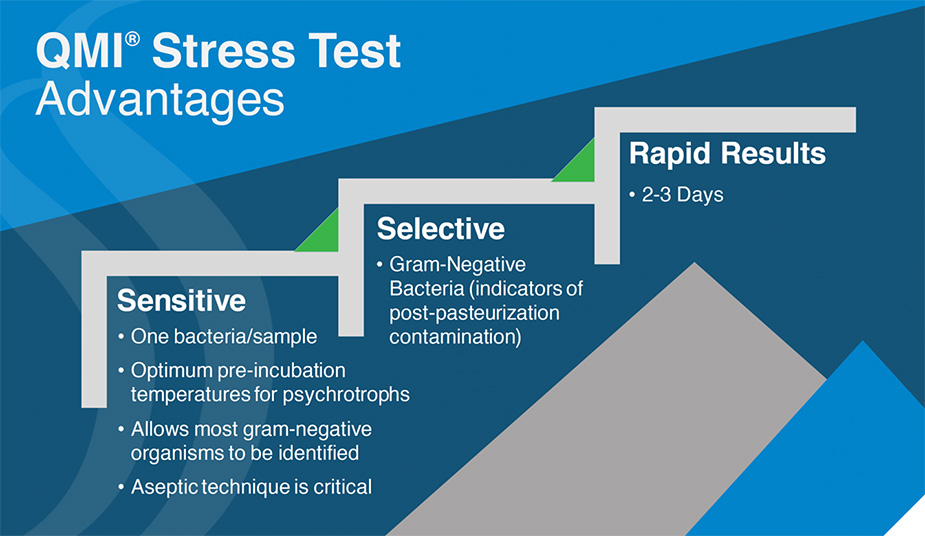
QMI Stress Test Procedure for Controlling Post-pasteurization Contamination
The patented QMI Stress Test is a proactive method to monitor CCP for post-pasteurization contamination. These CCP would include after high-temperature short time (HTSP), product storage tanks, and distribution valves before the filler.
QMI Stress Test Procedure
- Select and label the QualiTru TruMotion Collection Bag Part No. 111770-OP with CCP and date.
- For tank sampling, aseptically sample while the tank is being offloaded at an elbow near the tank using a QualiTru Collection Bag.
- For line sampling, aseptically obtain a large product sample using the two or five-liter QualiTru Collection Bag.
NOTE: The QualiTru TruMotion Collection Bag Part No. 111770-OP is oxygen permeable for optimal gram-negative growth and do NOT require adding headspace.
- Incubate the bagged sample at room temperature for 24 hours (for quick results) and again at 48 hours (for more accurate results).
- Do a plate count using a gram-negative selective media, such as Violet Red Bile Agar (VRB) or sodium deoxycholate, following the manufacturer’s recommended procedures (both are inhibitory to gram-positive bacteria).
- Incubate the plates at room temperature for 72 hours, observing for growth every 24 hours.
- The presence of any growth, Coliform or non-Coliform, indicates post-pasteurization contamination.
Presence of gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria do not survive pasteurization, so detecting their presence in process monitoring samples is a warning sign of post-pasteurization contamination that can lead to spoilage and food safety issues. A positive post-pasteurization test requires corrective action.
Read the following QualiTru blog posts to learn more:
- Psychrotrophic Bacteria in Pasteurized Milk—Spoilage, Testing, and Line Sampling
- Post-Pasteurization Contamination Monitoring: A Canary in the Coal Mine
Aseptic and representative sampling plays a vital role in monitoring milk quality and in-process monitoring for contamination within the dairy plant. Incorporating the QMI Stress Test as part of your regular quality control process will help identify critical contamination issues early.
Have questions about aseptic and representative sampling?
Need a quote? We’ll respond to
your request quickly.
Looking for one of our global distribution partners near you?
To learn more or to order please call 651-501-2337 or email us at [email protected]



